The Complete MBA Admissions Masterclass: Your 2025 Blueprint to Elite Business Schools
Introduction: Your Journey to Business School Excellence Starts Here

The MBA landscape has evolved dramatically in recent years, with new testing formats, shifting admissions criteria, and unprecedented competition for spots at top-tier programs. Whether you’re targeting the M7 schools (Harvard, Stanford, Wharton, Kellogg, Booth, Columbia, MIT Sloan), elite international programs like INSEAD and London Business School, or rising regional powerhouses, success requires more than just good grades and test scores.
This comprehensive guide synthesizes insights from admissions directors, successful applicants, and industry experts to provide you with a strategic roadmap for MBA admissions success in 2025. We’ll decode what schools really want, show you how to build a compelling narrative, and provide actionable timelines and strategies that have helped thousands of candidates secure their dream MBA offers.
Part 1: Mastering the MBA Admissions Game - What Top Schools Really Want
1.1 The Holistic Evaluation Framework: Beyond Numbers
Academic Excellence (25-30% of decision)
- GMAT/GRE scores demonstrating quantitative and analytical capability
- Undergraduate GPA showing consistent academic performance
- Transcript analysis revealing course rigor and grade trends
- Additional coursework or certifications addressing potential gaps
Professional Impact & Leadership (35-40% of decision)
- Quality and progression of work experience (typically 3-7 years preferred)
- Demonstrated leadership in professional settings
- Quantifiable achievements and business impact
- Industry diversity and career trajectory
- Entrepreneurial experience or intrapreneurial initiatives
Personal Qualities & Fit (20-25% of decision)
- Authentic personal story and motivation for MBA
- Clear post-MBA career goals aligned with school strengths
- Cultural fit with school values and community
- Unique background or perspective that adds diversity
- Communication skills and emotional intelligence
Community Contribution Potential (15-20% of decision)
- Extracurricular activities and volunteer work
- Leadership roles outside of work
- Potential to contribute to class discussions and school culture
- Alumni network engagement likelihood

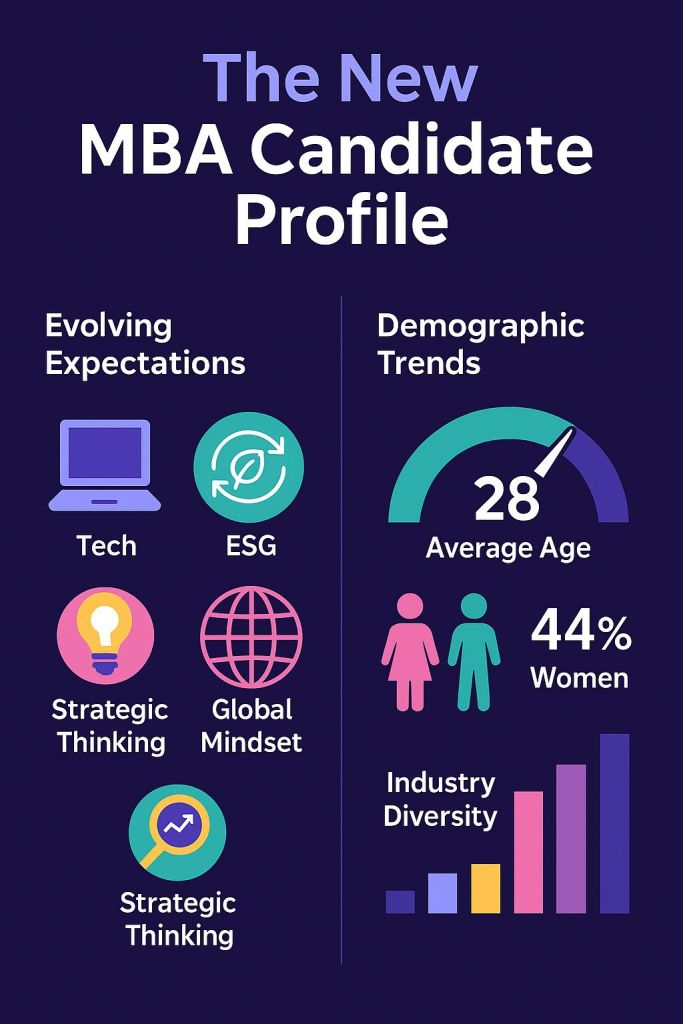
1.2 The New MBA Candidate Profile: What’s Changed in 2025
Evolving Expectations:
- Technology fluency: Schools increasingly value candidates with digital transformation experience
- ESG awareness: Environmental, social, and governance experience is highly valued
- Global mindset: International experience or cross-cultural competency is essential
- Adaptability: Post-pandemic resilience and change management experience
- Purpose-driven leadership: Clear alignment between personal values and career goals
Demographic Trends:
- Average age: 27-28 years (slight increase from previous years)
- Work experience: 4-6 years average, with quality valued over quantity
- International candidates: 35-45% of class composition at top programs
- Women representation: 45-50% target at most elite schools
- Industry diversity: Tech, consulting, and finance still dominant but healthcare, non-profit, and government gaining ground
1.3 Building Your Competitive Application Strategy
The Three-Pillar Approach:
Pillar 1: Academic Credibility
- Target GMAT Focus scores: 645+ (competitive), 685+ (strong), 715+ (exceptional)
- GPA enhancement strategies for candidates below 3.5
- Alternative transcript options and additional coursework
- Standardized test preparation timeline and retake strategies
Pillar 2: Professional Distinctiveness
- Career story arc development and positioning
- Leadership example identification and articulation
- Quantified impact measurement and presentation
- Promotion and responsibility progression demonstration
Pillar 3: Personal Authenticity
- Values-based narrative development
- Unique background and perspective leveraging
- Post-MBA goals clarity and feasibility
- School-specific fit demonstration


1.4 Application Component Deep Dive
Essays: Your Story, Your Impact
- Essay 1 (Goals/Why MBA): The 70-20-10 rule – 70% post-MBA goals, 20% why now, 10% why this school
- Essay 2 (Leadership/Impact): Use the STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result) with quantified outcomes
- Essay 3 (Personal/Background): Show vulnerability and growth, avoid generic statements
- School-specific essays: Demonstrate deep research and genuine interest
Recommendations: Third-Party Validation
- Supervisor recommendation: Focus on leadership, growth potential, and specific examples
- Client/peer recommendation: Highlight collaboration, influence, and 360-degree perspective
- Recommender briefing: Provide comprehensive packet with achievements, goals, and key messages
- Follow-up strategy: Ensure recommenders submit on time with quality content
Resume: Professional Snapshot
- Format: Reverse chronological with clear impact statements
- Content: Leadership roles, promotions, awards, quantified achievements
- Length: One page maximum with strategic white space usage
- Customization: Tailor for each school’s values and culture
Part 2: GMAT Focus Edition Mastery - Score Interpretation and Strateg
2.1 Understanding the New GMAT Focus Edition Landscape
Test Structure:
- Quantitative Reasoning: 21 questions, 45 minutes (Score range: 60-90)
- Verbal Reasoning: 23 questions, 45 minutes (Score range: 60-90)
- Data Insights: 20 questions, 45 minutes (Score range: 60-90)
- Total Score Range: 205-805 (calculated using a complex algorithm)
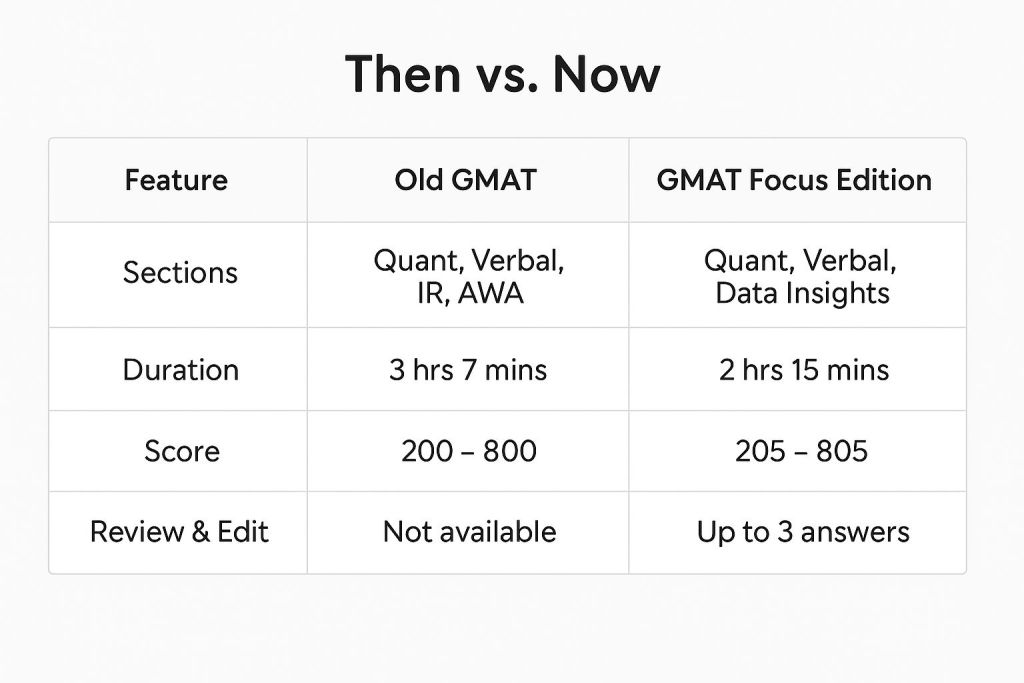
Key Changes from Previous GMAT:
- Elimination of Analytical Writing Assessment (AWA)
- Removal of Integrated Reasoning as separate section
- Introduction of Data Insights combining quantitative and verbal skills
- Shorter overall test duration
- Enhanced score reporting with percentile rankings
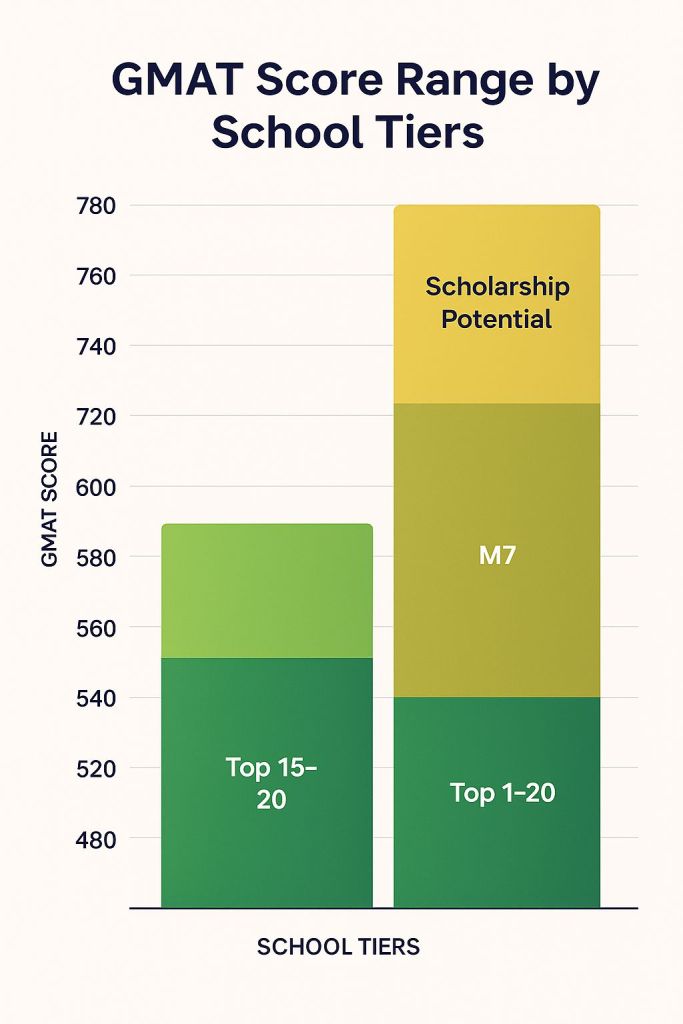
2.2 Score Benchmarking: What Your Numbers Really Mean
Score Interpretation Framework:
650-670 Range (65th-75th percentile:
- School Targets: Strong regional programs, international schools outside top 10
- Examples: Georgetown McDonough, Emory Goizueta, ESCP Europe, IE Business School
- Strategy: Excel in other application components, consider early application for scholarship opportunities
- Profile Compensation: Need exceptional work experience or unique background
675-690 Range (75th-85th percentile)
- School Targets: Top 15-20 programs, competitive international schools
- Examples: Rice Jones, BU Questrom, Imperial College London, HEC Paris
- Strategy: Solid foundation for competitive applications, focus on essay quality and school fit
- Profile Compensation: Good work experience and clear goals enhance candidacy significantly
695-715 Range (85th-95th percentile)
- School Targets: M7 schools, top international programs
- Examples: Kellogg, Booth, London Business School, INSEAD
- Strategy: Score opens doors, success depends on holistic profile strength
- Competitive Position: Above median for most top programs
720+ Range (95th+ percentile)
- School Targets: Any program globally, significant scholarship potential
- Examples: Harvard, Stanford, Wharton with strong scholarship consideration
- Strategy: Score provides competitive advantage, focus on unique value proposition
- Scholarship Impact: Likely to receive merit-based financial aid offers
2.3 Advanced Score Strategy and Retake Decisions
When to Retake Your GMAT:
- Current score is more than 20 points below school median
- Significant imbalance between sections (>10 point difference)
- Practice tests consistently showing 30+ point improvement potential
- Time allows for adequate preparation (minimum 6-8 weeks)
When NOT to Retake:
- Score is within 10 points of target school median
- Other application components need more attention
- Less than 4 weeks until application deadline
- Previous attempts show score plateau
Retake Preparation Strategy:
- Diagnostic analysis: Identify specific weaknesses through error logs
- Targeted preparation: Focus 80% of time on weakest areas
- Timing optimization: Practice under strict time constraints
- Official practice tests: Take 4-6 full-length practice exams
- Score reporting: Schools see all attempts, but most consider highest score

2.4 Beyond the Score: Contextualizing Your GMAT Performance
Factors Schools Consider:
- Educational background: Engineering/quantitative majors may need higher scores for balance
- Work experience: Strong professional track record can offset moderate scores
- Demographics: Underrepresented candidates may have different benchmarks
- International applicants: May need higher scores to demonstrate English proficiency
- Career goals: Consulting/finance career goals may require higher quantitative scores
Alternative Test Options:
- GRE General Test: Accepted by 95% of MBA programs, may suit certain learning styles better
- Executive Assessment: For executive MBA programs, shorter and more targeted
- GMAT vs GRE decision factors: Mathematical background, preparation time, school preferences
Part 3: Strategic School Selection - Building Your Optimal Application Portfolio
3.1 The Modern School Selection Framework
Tier-Based Application Strategy:
Reach Schools (2-3 applications)
- Programs where your stats fall below median but strong profile may compensate
- Focus on unique fit factors and exceptional essays
- Early round applications for best odds
- Examples: If you have 675 GMAT, consider Kellogg, Booth, or LBS
Target Schools (3-4 applications)
- Programs where your profile aligns well with admitted student averages
- Balance of academic rigor, career outcomes, and cultural fit
- Mix of rounds 1 and 2 for optimal positioning
- Examples: With 685 GMAT, target Duke Fuqua, NYU Stern, or UCLA Anderson
Safety Schools (1-2 applications)
- Programs where you exceed median statistics
- Strong scholarship potential and career outcomes
- Focus on maximizing financial aid and merit awards
- Examples: With 695 GMAT, consider Rice Jones, BU Questrom with scholarship focus
3.2 Comprehensive School Research Methodology
Academic Program Evaluation:
- Curriculum flexibility: Core requirements vs. elective options
- Specialization strength: Rankings and reputation in your career focus area
- Faculty quality: Research reputation and teaching excellence
- Class size and format: Large lectures vs. small seminars, case method vs. lecture style
- Global opportunities: International exchanges, study abroad options
Career Services Assessment:
- Employment statistics: 3-month post-graduation employment rates by industry
- Salary progression: Starting salaries and 5-year career trajectory data
- Alumni network strength: Geographic distribution and industry representation
- Recruiting relationships: On-campus recruiting statistics and company relationships
- Career coaching: Individual support and professional development resources
Cultural Fit Analysis:
- Student body composition: Age, experience, international representation, industry background
- Learning environment: Collaborative vs. competitive culture
- Extracurricular opportunities: Clubs, conferences, competitions, community service
- Location impact: Urban vs. suburban, industry proximity, lifestyle preferences
- Values alignment: School mission and your personal/professional values
3.3 International vs. Domestic Program Considerations
US MBA Programs – Advantages:
- Extensive alumni networks in major business centers
- Strong recruiting relationships with multinational corporations
- Optional Practical Training (OPT) and visa pathways for international students
- Diverse specialization options and research opportunities
- High starting salaries and career advancement potential
International MBA Programs – Advantages:
- Shorter program duration (12-16 months typical)
- Lower total cost of education and living expenses
- Global perspective and international business focus
- Language learning and cultural immersion opportunities
- Work authorization in multiple countries (EU programs)
Top International Programs to Consider:
- INSEAD (France/Singapore): Global brand, diverse cohort, 10-month program
- London Business School: Strong finance reputation, 15-21 month flexibility
- Oxford Saïd: One-year program, strong consulting outcomes
- Cambridge Judge: Entrepreneurship focus, small class size
- HEC Paris: French excellence, strong luxury/fashion industry connections
- IE Business School (Madrid): Innovation focus, strong technology connections
Part 4: Scholarship Mastery - Funding Your MBA Education
4.1 The Complete Scholarship Landscape
Merit-Based Scholarships:
Reach Schools (2-3 applications)
- Full tuition awards: Harvard Baker Scholar, Stanford Reliance Fellowship
- Partial tuition awards: 25-75% coverage, most common type
- Living stipends: Additional funding for living expenses, rare but valuable
- Automatic consideration: Many schools review all applicants automatically
- Separate applications: Some require additional essays or materials
Diversity and Leadership Scholarships:
- Forte Fellowship: $25,000-$40,000 for women in business, 50+ partner schools
- Consortium Fellowship: Full tuition for underrepresented minorities, 20+ member schools
- Robert Toigo Foundation: Finance-focused, networking and mentorship included
- MLT MBA Prep: Comprehensive support including scholarships and career coaching
- Reaching Out MBA: LGBTQ+ focused fellowship with financial and networking benefits
International and Government Scholarships:
- Fulbright Program: US citizens studying abroad, full funding including living expenses
- Chevening Scholarship: UK government funding for one-year programs
- DAAD Scholarships: German government funding for various European programs
- Erasmus Mundus: EU joint degree programs with full funding
- Commonwealth Scholarships: For citizens of Commonwealth countries studying in UK
Corporate and Industry Scholarships:
- McKinsey Emerging Scholars: Consulting focus with internship guarantee
- Goldman Sachs MBA Fellowship: Finance career track with mentorship
- Google MBA Scholarship: Technology leadership development
- Deloitte Graduate School Fellowship: Consulting and leadership development
- Military veterans programs: Yellow Ribbon, VR&E benefits, school-specific awards
4.2 Scholarship Application Strategy and Timeline
Research and Identification Phase (12-18 months before enrollment):
- Create comprehensive database of relevant opportunities
- Note application deadlines and requirements for each scholarship
- Identify recommenders and begin relationship building
- Start collecting required documentation and transcripts
Application Development Phase (6-12 months before enrollment):
- Craft compelling scholarship essays highlighting leadership and impact
- Secure strong letters of recommendation from appropriate sources
- Complete financial aid forms and documentation
- Submit early applications to maximize consideration
Selection and Interview Phase (3-9 months before enrollment):
- Prepare for scholarship interviews with mock sessions
- Research program details and articulate clear post-MBA goals
- Demonstrate knowledge of scholarship sponsor and their values
- Follow up appropriately and maintain professionalism throughout
Negotiation and Decision Phase (1-6 months before enrollment):
- Compare total financial packages including scholarships, loans, and grants
- Negotiate with schools using competing offers when appropriate
- Consider long-term career impact vs. short-term financial benefits
- Make informed decisions about program and funding combinations
4.3 Financial Aid and Loan Optimization
Federal Financial Aid (US Citizens/Permanent Residents):
- FAFSA completion: File as early as possible for maximum aid consideration
- Stafford Loans: Up to $20,500 per year, subsidized and unsubsidized options
- Graduate PLUS Loans: Cover remaining costs after other aid, higher interest rates
- Work-study programs: Part-time employment opportunities on campus
- Tax benefits: American Opportunity and Lifetime Learning Credits
Private Loan Options:
- School-sponsored loans: Often better rates and terms than commercial options
- Bank and credit union loans: Compare rates, terms, and repayment options
- International student loans: Specialized products for non-US citizens
- Cosigner requirements: Impact on rates and approval odds
- Variable vs. fixed rates: Interest rate risk and payment predictability
Creative Funding Strategies:
- Employer sponsorship: Tuition reimbursement and sabbatical programs
- Consulting during school: Part-time work with former employers or clients
- Teaching assistantships: Tuition reduction in exchange for teaching support
- Research assistantships: Work with faculty on research projects
- Entrepreneurship grants: Funding for business plan competitions and startups
Part 5: Application Timeline and Project Management
5.1 The 18-Month MBA Application Roadmap
Phase 1: Foundation Building (18-12 months before applications)
Month 1-2: Initial Assessment and Planning
- Complete diagnostic GMAT/GRE practice test
- Evaluate undergraduate transcripts and identify any gaps
- Conduct initial career goals assessment and research
- Begin building relationship with potential recommenders
- Research target schools and create preliminary list
Month 3-4: Test Preparation Launch
- Enroll in GMAT/GRE preparation program or develop self-study plan
- Begin consistent study schedule (15-20 hours per week minimum)
- Take first official practice test to establish baseline
- Consider additional coursework if undergraduate GPA needs strengthening
- Start attending MBA information sessions and networking events
Month 5-6: Intensive Test Preparation
- Continue structured test preparation with increased intensity
- Take second and third practice tests to track progress
- Consider test date scheduling based on preparation progress
- Begin informal discussions with potential recommenders
- Conduct informational interviews with alumni from target schools
Phase 2: Application Development (12-6 months before applications)
Month 7-8: Test Completion and School Research
- Take first official GMAT/GRE attempt
- Analyze score and determine retake necessity
- Finalize target school list with reach/target/safety balance
- Begin detailed research on each target school’s culture and programs
- Attend virtual or in-person school information sessions
Month 9-10: Essay Development and Recommender Preparation
- Begin essay brainstorming and outline development for each school
- Create comprehensive recommender briefing packets
- Formally request recommendations with clear timelines
- Consider hiring admissions consultant if needed for essay support
- Begin resume updates and formatting for business school applications
Month 11-12: Content Creation and Refinement
- Complete first drafts of all required essays
- Provide recommenders with final briefing materials and deadlines
- Finalize resume with quantified achievements and leadership examples
- Begin scholarship research and application preparation
- Consider campus visits or virtual events for top choice schools
Phase 3: Application Execution (6-0 months before deadlines)
Month 13-14: Application Assembly and Review
- Complete final essay drafts with multiple rounds of editing
- Finalize all application forms and supplementary materials
- Confirm recommender submission status and provide gentle reminders
- Complete scholarship applications with required essays and documentation
- Conduct final application review for completeness and consistency
Month 15-16: Submission and Interview Preparation
- Submit Round 1 applications by October deadlines
- Begin interview preparation with mock sessions and school research
- Complete any remaining Round 2 applications for January deadlines
- Monitor application status and respond to any requests for additional information
- Continue scholarship applications with upcoming deadlines
Month 17-18: Interview Season and Decision Management
- Conduct admissions interviews with confidence and preparation
- Submit any final Round 3 applications for March/April deadlines
- Compare admission offers and financial aid packages
- Make final enrollment decisions and submit deposits
- Begin pre-MBA preparation including networking and skill building
5.2 Critical Deadlines and Milestones
Round 1 Applications (September-October 2024):
- Advantages: Higher acceptance rates, maximum scholarship consideration, demonstrated interest
- Best for: Strong candidates ready to apply, career changers needing early confirmation
- Typical deadlines: September 15 – October 15, varying by school
- Notification: December – January, allowing time for Round 2 if needed
Round 2 Applications (January 2025):
- Advantages: Most popular round, good acceptance rates, adequate scholarship opportunities
- Best for: Majority of candidates, those needing extra preparation time
- Typical deadlines: January 5 – January 15, very tight window after holidays
- Notification: March – April, standard admission timeline
Round 3 Applications (March-April 2025):
- Advantages: Final opportunity, less competitive pool, potential for waitlist movement
- Best for: Strong candidates who missed earlier rounds, international applicants
- Typical deadlines: March 15 – April 30, varies significantly by school
- Notification: May – June, tight timeline for enrollment decisions
Rolling Admissions Programs:
- Process: Applications reviewed as received until class is full
- Strategy: Apply as early as possible for best odds and scholarship consideration
- Examples: Some part-time and executive programs use rolling admissions
- Timeline: Can extend from fall through summer before enrollment
5.3 Application Management and Organization Systems
Digital Organization Tools:
- Spreadsheet tracking: Deadlines, requirements, status updates for each school
- Document management: Cloud storage for essays, transcripts, recommendations
- Calendar integration: Important deadlines and milestone reminders
- Password management: Secure storage for application login credentials
- Backup systems: Multiple copies of all important documents and essays
Quality Control Processes:
- Essay review cycles: Multiple drafts with feedback from various sources
- Application checklists: Detailed requirements verification for each school
- Proofreading protocols: Professional editing and multiple review rounds
- Submission verification: Confirmation of successful application submission
- Follow-up procedures: Monitoring application status and responding to requests
Part 6: Advanced Strategies for Competitive Advantage
6.1 Building Your Personal Brand for MBA Admissions
Digital Presence Optimization:
- LinkedIn profile: Professional headline, compelling summary, detailed experience descriptions
- Professional website: Portfolio of achievements, leadership examples, career narrative
- Social media audit: Review and clean up personal social media presence
- Content creation: Industry insights, leadership perspectives, career journey sharing
- Network engagement: Meaningful interactions with MBA communities and professionals
Thought Leadership Development:
- Industry publications: Write articles or blog posts about your field of expertise
- Speaking opportunities: Conferences, panels, company presentations, podcast appearances
- Professional associations: Leadership roles in industry or functional organizations
- Mentoring activities: Formal or informal mentoring of junior colleagues or students
- Community involvement: Board positions, volunteer leadership, social impact initiatives
6.2 Addressing Application Weaknesses and Red Flags
Low Undergraduate GPA (Below 3.0):
- Strategy: Additional coursework, professional certifications, quantified work achievements
- Explanation: Brief, honest acknowledgment in optional essay without making excuses
- Compensation: Exceptional GMAT scores, strong work progression, leadership examples
- Timeline: Take relevant courses 1-2 years before application to show recent academic success
Limited Work Experience (Less than 3 Years):
- Strategy: Emphasize leadership impact, accelerated progression, unique experiences
- Enhancement: Seek additional responsibilities, cross-functional projects, leadership roles
- Alternative paths: Consider deferred admission programs or gap year with targeted experience
- Positioning: Focus on potential and learning agility rather than extensive experience
Career Change or Unclear Goals:
- Strategy: Articulate clear logical progression and transferable skills
- Research: Deep industry knowledge and realistic career path understanding
- Networking: Connections in target industry to validate career change feasibility
- Experience: Relevant projects, volunteering, or part-time work in target field
Weak Recommendation Letters:
- Prevention: Choose recommenders who know your work well and can provide specific examples
- Briefing: Comprehensive packet with achievements, goals, and key messages to emphasize
- Alternative options: Former clients, mentors, or board members if supervisors unavailable
- Timing: Request recommendations early and provide adequate time for thoughtful responses
6.3 Interview Excellence and Preparation
Interview Format Preparation:
- Traditional interviews: One-on-one with admissions staff or alumni
- Panel interviews: Multiple interviewers asking questions in sequence
- Group interviews: Multiple candidates in group discussion or presentation format
- Video interviews: Technical preparation and professional setup considerations
- Case interviews: Business problem-solving with structured approach
Core Interview Question Categories:
- Walk me through your resume: Concise career narrative with key achievements
- Why MBA, why now, why here: Clear goals alignment with program strengths
- Leadership example: Specific situation with measurable impact and learning
- Teamwork challenge: Collaboration skills and conflict resolution abilities
- Ethical dilemma: Values-based decision making and moral reasoning
- Questions for us: Thoughtful inquiries demonstrating genuine interest and research
Advanced Interview Strategies:
- Storytelling framework: Compelling narratives with clear structure and impact
- School-specific research: Deep knowledge of programs, culture, and opportunities
- Behavioral interview preparation: STAR method for consistent, comprehensive responses
- Mock interview practice: Multiple sessions with different question styles and interviewers
- Follow-up protocol: Thank you notes and continued interest demonstration
Part 7: Post-Application Success and Enrollment Preparation
7.1 Managing Admissions Decisions and Waitlist Strategy
Acceptance Management:
- Scholarship negotiation: Leverage competing offers professionally and strategically
- Program comparison: Detailed analysis of career outcomes, culture, and opportunities
- Deposit deadlines: Understand commitment requirements and timing
- Pre-MBA networking: Connect with admitted students and begin relationship building
- Preparation planning: Skills development, reading lists, and knowledge building
Waitlist Navigation:
- Additional materials: Updated resume, recent achievements, continued interest letter
- Relationship building: Appropriate contact with admissions office and current students
- Alternative planning: Backup plans and gap year productive activity consideration
- Patience and persistence: Professional follow-up without becoming bothersome
- Timeline awareness: Waitlist movement typically occurs through summer months
Rejection Analysis and Reapplication:
- Feedback seeking: Request constructive feedback from admissions offices when possible
- Profile strengthening: Identify specific areas for improvement over gap year
- School strategy revision: Consider different target schools or application approach
- Timeline planning: Year-long development plan for stronger reapplication
- Professional support: Consider admissions consulting for reapplication strategy
7.2 Pre-MBA Preparation and Skill Building
Academic Preparation:
- Quantitative skills: Statistics, accounting, finance fundamentals if lacking background
- Case study practice: Harvard Business School case method preparation
- Reading lists: School-recommended books and industry publications
- Language skills: International programs may require additional language preparation
- Technology proficiency: Excel, PowerPoint, and analytical software familiarity
Professional Development:
- Industry networking: Continued relationship building in target post-MBA field
- Skill certifications: Relevant professional certifications or online courses
- Leadership experience: Additional volunteer or professional leadership opportunities
- Global experience: International travel or work experience if lacking
- Entrepreneurship: Side projects or business ventures to demonstrate initiative
Personal Preparation:
- Financial planning: Budgeting for program costs and living expenses
- Life logistics: Housing, family considerations, and personal arrangements
- Health and wellness: Physical and mental health preparation for intensive program
- Relationship management: Communication with family and friends about program demands
- Goal refinement: Continued clarity development about post-MBA objectives
Conclusion: Your Path to MBA Success Starts Now
The journey to MBA admission at top programs requires strategic planning, exceptional execution, and unwavering commitment to excellence. Success isn’t just about achieving high test scores or impressive work experiences—it’s about crafting a compelling narrative that demonstrates your unique value proposition and potential for leadership impact.
The MBA landscape continues to evolve, with schools seeking candidates who can navigate complex global challenges, drive innovation and change, and contribute meaningfully to diverse learning communities. Your application must not only meet academic and professional standards but also showcase your authentic self and clear vision for how an MBA will accelerate your ability to create positive impact.
Key Success Factors to Remember:
- Start Early and Plan Strategically: The most successful candidates begin their MBA journey 18-24 months before intended enrollment, allowing adequate time for test preparation, school research, relationship building, and application development.
- Focus on Fit, Not Just Rankings: While prestigious programs offer tremendous value, the best MBA experience comes from choosing schools where your goals, values, and learning style align with the program’s strengths and culture.
- Tell Your Unique Story: Admissions committees review thousands of applications from accomplished professionals. Your differentiator lies in your unique background, perspective, and potential for future impact.
- Invest in Quality: Whether it’s test preparation, essay editing, or interview coaching, strategic investments in your application quality can yield significant returns in admission outcomes and scholarship opportunities.
- Build Authentic Relationships: MBA programs are fundamentally about people and networks. Start building genuine relationships with alumni, current students, and admissions teams early in your journey.
- Prepare for the Long Game: MBA admission is just the beginning. Your real success will be measured by how effectively you leverage your MBA experience to achieve your career goals and create meaningful impact.
The competition for spots at top MBA programs has never been more intense, but neither have the opportunities for exceptional candidates who approach the process with strategy, authenticity, and determination. Use this guide as your roadmap, but remember that your journey will be unique to your goals, background, and aspirations.
Ready to Begin Your MBA Journey?
Your future starts with the first step. Whether that’s taking a diagnostic GMAT, researching target schools, or beginning conversations with potential recommenders, the most important decision is to start today. The MBA candidates who achieve their dreams are those who combine exceptional preparation with authentic self-presentation and unwavering commitment to their goals.
The path ahead is challenging but extraordinarily rewarding. With the right strategy, dedicated preparation, and genuine passion for growth and impact, you can join the ranks of MBA graduates who are shaping the future of business and society.
Your journey to business school excellence begins now. Make it count.
Additional Resources and Next Steps
GMATOrb Premium Services:
- Diagnostic Assessment: Comprehensive evaluation of your MBA readiness and application strategy
- GMAT Mastery Program: Personalized test preparation with score improvement guarantee
- Application Consulting: Expert guidance on school selection, essay development, and interview preparation
- Scholarship Optimization: Specialized support for merit-based and diversity scholarship applications
Connect With Our Experts:
- Email: [email protected] for personalized consultation
- Website: www.gmatorb.com for additional resources and tools
- Community: Join our MBA candidate community for peer support and insights
- Blog: Regular updates on admissions trends, test strategies, and success stories
Recommended Timeline Actions:
- Today: Take our free diagnostic assessment to establish your baseline
- This Week: Research 10-15 target schools and create initial comparison spreadsheet
- This Month: Begin GMAT preparation and identify potential recommenders
- Next 90 Days: Complete first official GMAT attempt and begin essay brainstorming
- Next 6 Months: Submit first round applications with comprehensive preparation
Your MBA success story starts with the decision to pursue excellence. Let GMATOrb be your trusted partner in achieving your business school dreams and launching the next chapter of your professional journey.

